Mục lục
1. What is periodontal disease ?
Periodontal disease is an infection that affects the tissues and bone supporting teeth. When someone has periodontal disease, the gum tissue pulls away from the tooth. If the condition becomes worse, the tissue and the bone that support teeth are destroyed. Then teeth may be shifting and fall out.
2. What causes periodontal diseases?
Periodontal diseases are caused by plaque, a sticky film that forms on your teeth. It includes bacteria that produce harmful toxins. The toxin can irritate and inflame the gums if teeth are not cleaned. If plaque stays on teeth for long time, it can harden into a rough surface called tartar.
Inflamed gums can pull away from teeth and form spaces called pockets. The pockets trap plaque, tartar and bacteria that you cannot remove by brushing. Then the gums become infected, the bone and other tissues that support teeth are damaged.
3. How do periodontal diseases develop ? Stages of Periodontal Diseases
- Healthy gums (Normal)
Teeth are held firmly by the gums, bone and periodontal ligament. There is little or no plaque and tartar.
- Gingivitis (Disease)
If the plaque is not removed, it can harden into tartar. The bacteria in plaque and tartar irritate the gums and make them red, swollen and likely to bleed.
- Periodontitis (Disease)
As plaque and tartar build up along the gumline, bacteria break down the soft and bone tissue.
4. How do I know if I have periodontal disease?
Several warning signs can signal a problem. If you notice any of the following, see your dentist:
- Gums that bleed when you brush or floss
- Red, swollen and tender gums
- Gums that have pulled away from teeth
- Bad breath that doesn’t go away
- Pus between the teeth and gums
- Loose or separating teeth
- A change in the way your teeth fit together when you bite
- A change in the fit of partial dentures
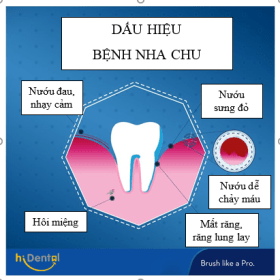
However, you can have periodontal disease and not notice any of mentioned signs. That is why regular dental checkups are very important
5. Relationship between periodontal disease and systematic health
Tooth loss is not the only possible problem of periodontal disease. There may be a link between periodontitis and cardiovascular disease (heart disease and stroke). High stress may also be linked to periodontal diseases.
References:
- ADA – American Dental Association (2012)
- Oral B


 日本語
日本語 VI
VI